Good oral health is crucial for overall well-being, and one of the early warning signs of potential issues is bleeding gums. While it might seem like a minor inconvenience, persistent gum bleeding could be an indication of gum disease, a common but often overlooked condition. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various aspects of gum disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options.
Understanding Gum Disease
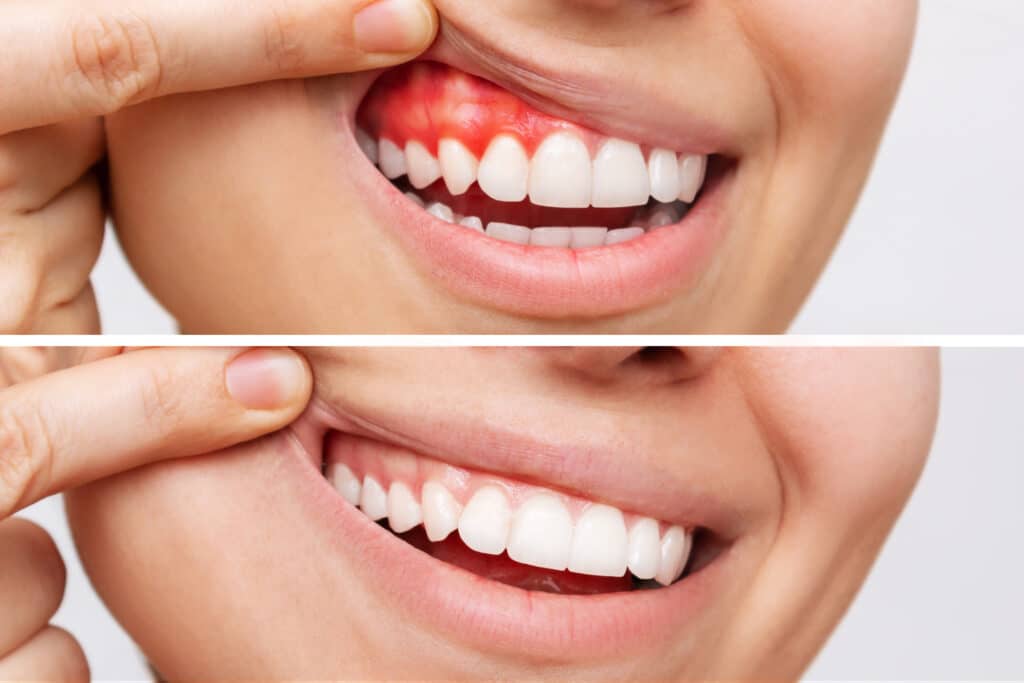
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an inflammatory condition affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. It typically starts with the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth and gums. If not adequately removed through regular oral hygiene practices like brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to irritation and inflammation of the gums. This early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis.
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. Periodontitis involves the inflammation of the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. As the condition advances, pockets may form between the teeth and gums, leading to further bacterial growth and potential tooth loss.
Stages of Gum Disease
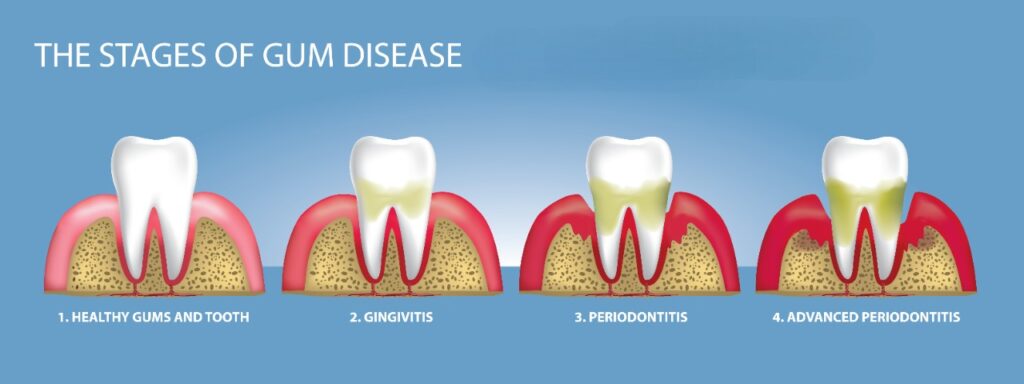
| Stage | Description | Symptoms |
| Gingivitis (Early Stage) | Inflammation of the gums, reversible with good oral hygiene. | Red, swollen, and bleeding gums. |
| Mild Periodontitis | Early bone loss, usually treatable with professional cleaning and improved hygiene. | Deeper pockets around teeth, slight gum recession. |
| Moderate Periodontitis | Significant bone loss, teeth becoming loose. | Increased gum recession, loose teeth, pus between teeth. |
| Severe Periodontitis | Advanced bone loss, possible tooth loss. | Severe gum recession, loose teeth, deep pockets, pain. |
Causes of Gum Disease
Several factors contribute to the development of gum disease. Understanding these causes is essential for effective prevention and management
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, leading to gum inflammation.
Tobacco Use
Smoking or using tobacco products increases the risk of gum disease and can hinder the effectiveness of treatment.
Genetic Predisposition
Some individuals may be more genetically susceptible to gum disease
Poor Nutrition
A diet lacking in essential nutrients can weaken the immune system and compromise gum health.
Medical Conditions
Certain systemic conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of gum disease.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause, can make gums more susceptible to inflammation.
Certain Medications
Some medications, such as antihypertensive drugs and antipsychotics, may have side effects that impact oral health.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Bleeding gums are a primary indicator of gum disease, but they are not the only symptom. Being aware of the following signs can help in early detection
Gum Bleeding
Especially during brushing or flossing.
Swollen or Tender Gums
Inflammation and tenderness are common early signs.
Persistent Bad Breath
Bacteria associated with gum disease can cause chronic bad breath
Receding Gums
Gums that pull away from the teeth, making them appear longer.
Changes in Tooth Alignment
Shifting or loosening of teeth as the supporting structures weaken.
Pain While Chewing
Discomfort or pain while eating may indicate advanced gum disease.
Pus Between Teeth and Gums
A clear sign of infection that requires immediate attention.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Ignoring the early signs of gum disease can have serious consequences. Gingivitis, if left untreated, can progress to periodontitis, leading to irreversible damage to the supporting structures of the teeth. Eventually, this may result in tooth loss. Moreover, there is increasing evidence linking gum disease to systemic health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems
Preventing Gum Disease
Prevention is the cornerstone of maintaining good oral health. Here are some key strategies to prevent gum disease
Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
Brush teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent its accumulation
Regular Dental Checkups
Routine dental examinations and cleanings are crucial for early detection and intervention.
Healthy Diet
Consume a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support gum health.
Avoid Tobacco Products
Quitting smoking or using tobacco products can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to gum disease, so adopting stress-management techniques is beneficial.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake can contribute to poor oral health, so moderation is key.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
If gum disease is diagnosed, various treatment options are available, depending on the severity of the condition
Professional Dental Cleaning
Scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure, can remove tartar and bacteria from below the gumline.
Medications
Antibiotics or antimicrobial mouthwashes may be prescribed to control bacterial infection.
Surgical Procedures
In advanced cases, surgical interventions such as flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts may be necessary.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthier lifestyle, including improved oral hygiene and dietary changes, is crucial for long-term management.
Foods for Gum Health
| Food | Benefit |
| Leafy greens | Rich in vitamins and minerals essential for gum health. |
| Citrus fruits | Vitamin C boosts immune system and collagen production. |
| Berries | Antioxidants may reduce inflammation and fight infection. |
| Nuts and seeds | Good source of vitamin E and healthy fats. |
| Yogurt | Probiotics may help combat harmful bacteria in the mouth. |
Tips for Preventing Gum Disease
| Tip | Description |
| Brush twice daily and floss once daily | Removes plaque and bacteria. |
| Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing technique | Avoid damaging gums. |
| Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups | Professional care is crucial. |
| Quit smoking | Improves overall health and reduces gum disease risk. |
| Eat a healthy diet | Supports oral health and overall well-being. |
Conclusion
Bleeding gums should never be ignored, as they may be an early warning sign of gum disease—a condition that, if left untreated, can have serious consequences for oral and overall health. Maintaining good oral hygiene, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking professional dental care are essential steps in preventing and managing gum disease. Remember, your oral health is an integral part of your overall well-being, and addressing any issues promptly can contribute to a healthier, happier life. If you’re experiencing persistent gum bleeding or other symptoms, consult with your dentist for a comprehensive evaluation and personalised advice from Parkmore Family Dental.